Trump Fights Back After Cases Against Comey and James Dismissed: Live
Legal Challenges and Political Maneuvers
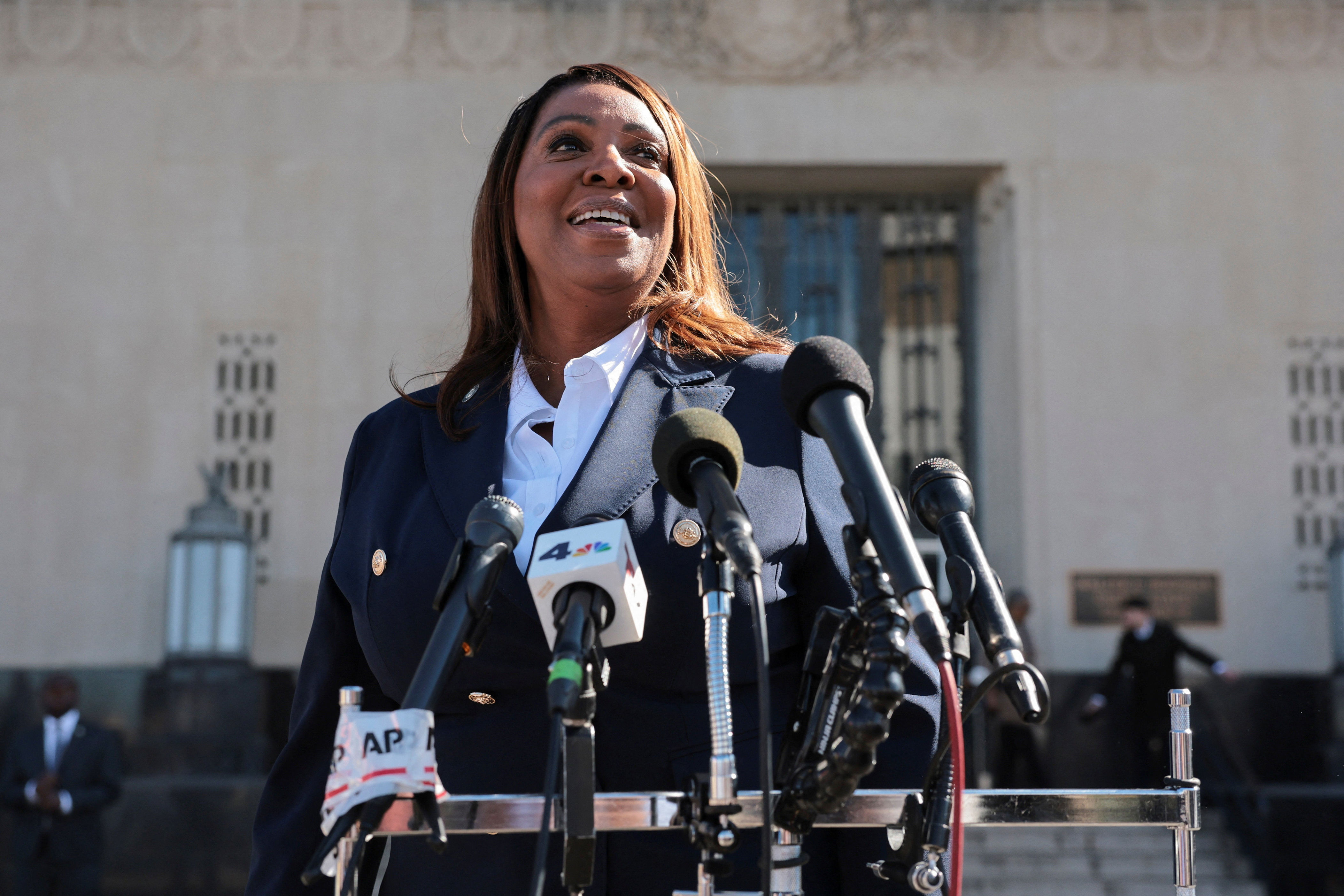
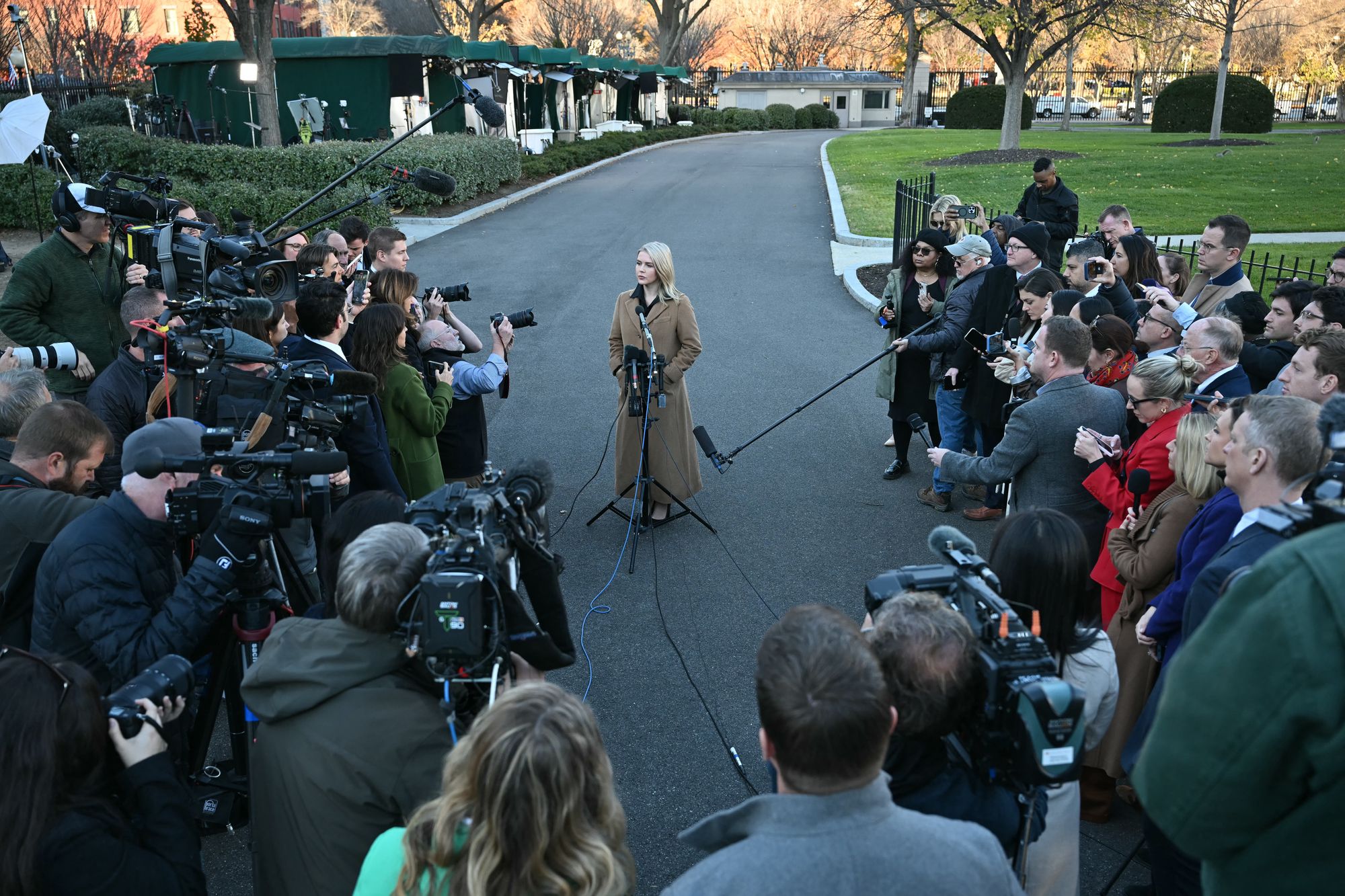
The Trump administration has faced a significant legal setback after a federal judge dismissed criminal cases against former FBI Director James Comey and New York Attorney General Letitia James. The ruling came as a result of the unlawful appointment of interim U.S. Attorney Lindsey Halligan, who had signed off on the cases. White House Press Secretary Karoline Leavitt expressed confidence in the legitimacy of Halligan's appointment and indicated that the Department of Justice would appeal the decision.
Comey and James are among several high-profile figures targeted by investigations under the Trump administration. These cases have sparked considerable debate over the use of the Justice Department to pursue political enemies.
Pentagon Investigation into Senator Mark Kelly
In another development, the Department of Defense has launched an investigation into Democratic Senator Mark Kelly following his participation in a video encouraging active military service members to ignore orders that violate the Constitution. Kelly, a retired naval officer, is the only one of the five Democrats involved in the video who falls under the jurisdiction of the Department of Defense. This has led to a "thorough review" of potential misconduct, with the department stating it will ensure due process and impartiality.
Kelly responded to the investigation by asserting that he would not be intimidated and that he would continue to hold the administration accountable. He emphasized his long-standing commitment to the country and its constitutional values.
Trump's AI Initiative and International Relations
President Donald Trump has also taken steps to advance technological innovation through an executive order establishing the "Genesis Mission," an initiative aimed at leveraging artificial intelligence to merge scientific data across federal agencies. This effort is expected to significantly accelerate research and development, particularly in the fields of drug discovery and other major breakthroughs.
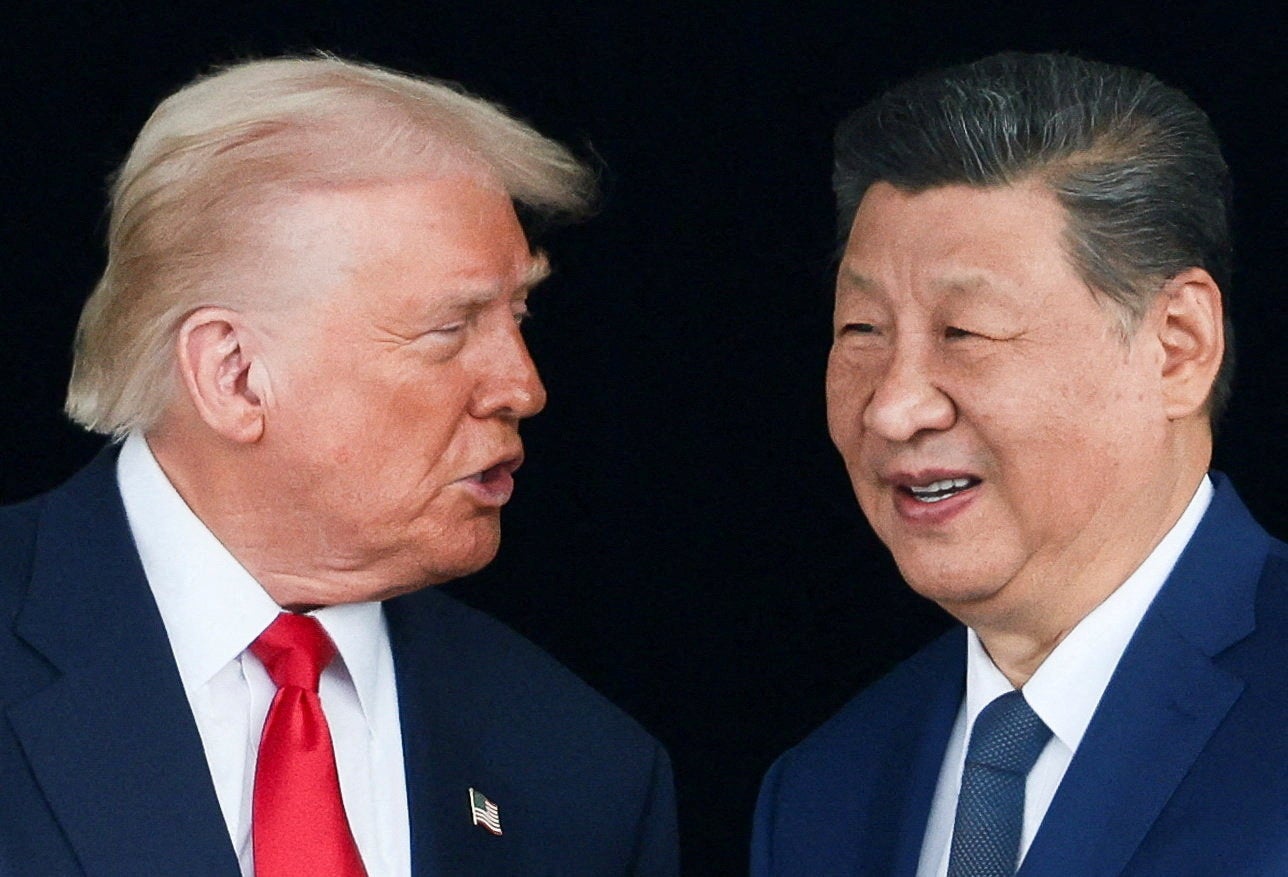
In addition, Trump announced plans for a visit to Beijing in April and a state visit from Chinese President Xi Jinping later in 2026. This follows a "very good" call between the two leaders, which covered topics such as trade, Taiwan, and the proposed peace deal for the Ukraine-Russia conflict.
Internal Struggles Within the Republican Party
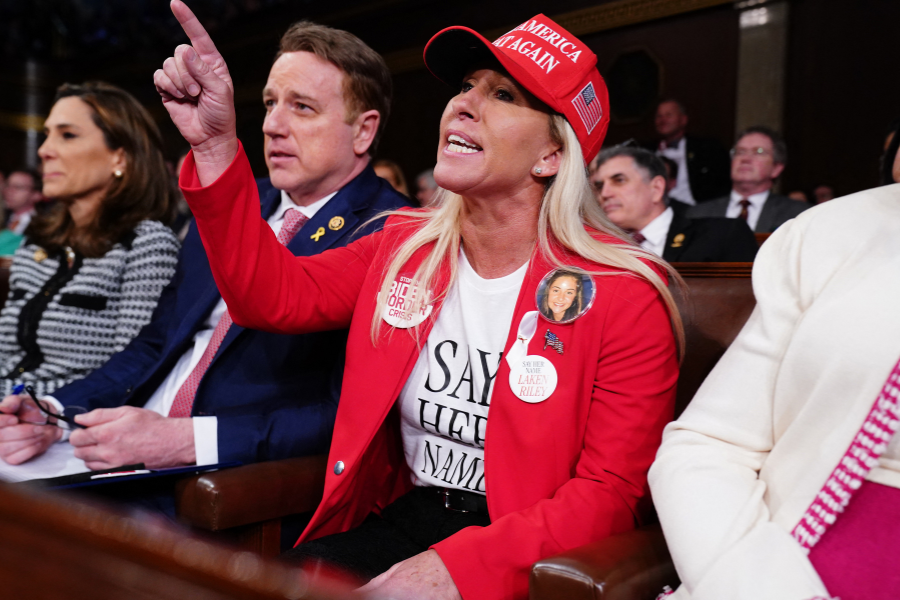
Marjorie Taylor Greene, a prominent Republican figure, has announced her resignation from Congress, citing growing tensions with the president. This move has prompted speculation about whether other GOP lawmakers might follow suit. Reports suggest that morale within the party is low, with some considering early retirements.
Greene's departure has also raised questions about her future political aspirations, although she has denied any plans to run for president in 2028.
Public Sentiment and Economic Concerns
Public sentiment regarding the economy remains mixed, with many Americans expressing concerns over the cost of living. A recent poll revealed that four in ten Republicans believe Trump is sugarcoating the impact of inflation and rising prices. Despite these concerns, the administration continues to tout record-low gas prices ahead of the Thanksgiving travel season, though data suggests prices were actually lower last year.
Other Developments
Other notable developments include the suspension of operations by the Gaza Humanitarian Foundation, a controversial group backed by both the U.S. and Israel. Additionally, the Trump administration is reportedly preparing to announce a new healthcare proposal aimed at making medical care more affordable for Americans.
As the administration continues to navigate a complex landscape of legal challenges, political maneuvering, and public sentiment, the focus remains on how these developments will shape the future of American politics and policy.

Legal and Political Implications
The dismissal of the indictment against James Comey and Letitia James highlights the ongoing legal battles within the Trump administration. The ruling underscores the importance of proper appointments and the potential consequences of procedural errors. The White House's response to this decision reflects the administration's determination to challenge the ruling and continue its efforts to target political opponents.
In contrast, the investigation into Senator Mark Kelly illustrates the broader implications of the administration's actions. The Pentagon's involvement in this matter signals a shift in how the administration is addressing perceived threats to its policies and leadership.
Media and Public Discourse
The media landscape continues to play a critical role in shaping public perception of the administration. From the release of the Genesis Mission to the ongoing discussions about the Ukraine-Russia conflict, the press remains a key player in disseminating information and influencing public opinion.
Additionally, the administration's rhetoric towards Democrats has drawn criticism from within its own party, with some Republicans urging a more measured approach. This internal tension highlights the complexities of maintaining unity while pursuing a specific political agenda.
Conclusion
As the Trump administration faces a series of legal and political challenges, the focus remains on how these issues will impact the broader landscape of American politics. From the dismissal of indictments to the investigation of a senator, each development contributes to the evolving narrative of the administration's tenure. With the upcoming presidential election looming, the stakes have never been higher for both the administration and its critics.